As a kind of smart card, the SIM card is still limited in terms of data storage and encryption and decryption processing.
In the early days of mobile communication, there was no concept of SIM card. At that time, the method of integrated machine number was adopted. (Later, for the CDMA technology, the concept of machine card separation and machine card integration appeared. There is no concept of SIM card in the early stage, so there is no way to talk about it. Starting the machine card), you need to match the number and the phone by burning the number (in a sense, writing a certain storage area of ​​the phone to the specified data content). The early big brothers in China were this way, and later PHS had used this method. The disadvantage is that it is cumbersome to replace the mobile phone, and because of the burning operation, the phenomenon of downtime is widespread, and the mobile phone is stolen.
Therefore, it is necessary to find a more secure storage carrier to store these sensitive information and perform certain encryption and decryption functions.
Just at this time, smart card technology began to mature. Therefore, people naturally hope to use smart cards to improve the security flaws in the original mobile communication. So the European Telecommunications Standardization Committee ETSI has developed a series of standards for SIM cards. The data content and format that need to be stored in the SIM card are described in detail, and the role that the SIM card should play in the user's use of the mobile network service.
In the mobile network, the SIM card mainly has three functions: user identity authentication, data information storage, and STK to provide value-added services.
From the appearance, the SIM card is divided into a large card (ID-1 card, the size is the same as the credit card), and a small card (Plug-in card, the portion of the SIM card that has been punched and cut). In addition to the early mobile phones supporting large cards, almost all mobile phones currently only support small cards.
The authentication of the GSM network uses the Comp128-1/2/3 algorithm, also known as the A3A8 algorithm. The CDMA algorithm uses the CAVE algorithm, and the 3G network uses the MILENAGE algorithm. Although there are differences in specific algorithms, the authentication process is similar. The main authentication process is as follows:
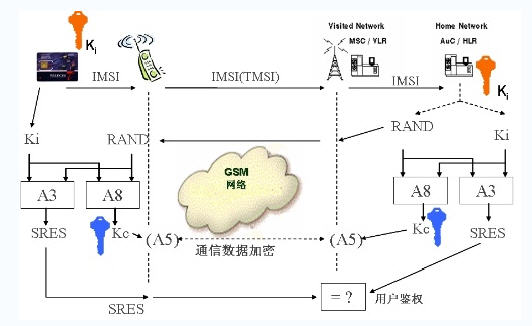
SIM card authentication process
The International Mobile Subscriber Indentity (IMSI) and the Key Ki are secret data that need to be stored securely. If the IMSI and Ki are leaked, the SIM card is deciphered, usually using the Comp128-1 algorithm. The SIM card takes about 3-10 hours to be deciphered by collision attack, and there is currently no effective deciphering method for the Comp128-2/3 algorithm.
When the authentication is performed, a random number RAND is generated from the network, and the authentication result SRES and the session encryption key Kc are calculated by using the IMSI and Ki stored in the SIM card. If the SRES calculated by the SIM card is the same as the SRES calculated by the network, the authentication succeeds. . Because mobile phone users can roam, the main network elements participating in the authentication include the Visited Location Register (VLR), the Mobile Switching Center (MSC), the Home Location Register (HLR), and the Authentication Center. AuC (Authentication Center).
When the mobile phone is turned on, it first reads a series of service information stored in the SIM card, and then performs network authentication. If the authentication succeeds, the current operator name is displayed, and the user can perform normal operations. . In order to prevent the user from unplugging the SIM card after logging in, the mobile phone will send a query command within a certain time interval to check the current status of the SIM card. Once the SIM card is found to have not sent back the correct response, the connection between the network and the network is cut off. , prompt to insert the SIM card. Due to the matching problem between some SIM cards and mobile phones, it is obvious that the SIM card inserted in the mobile phone will also prompt "insert SIM card" because the mobile phone does not get the correct SIM card response during the inquiry.
The following figure depicts the main file contents stored in the SIM card, where SMS is a short message file and ADN is a phone book file. The meaning of other documents is defined in detail in the ETSI 11.11 specification.
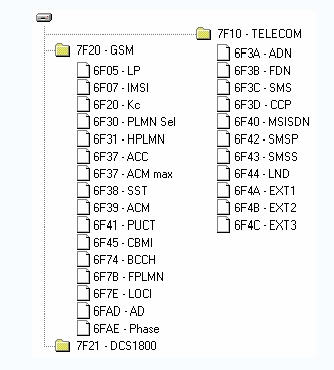
SIM card file content diagram
Watch Travel Case ,Custom Watch Case,Eva Watch Case,Eva Hard Watch Case
Shenzhen Guohui Craft Products Co.,Ltd. , https://www.evacarrycase.com