Proteins, peptides, carbohydrates, nucleic acids, lipids, and many other naturally occurring or synthetic compounds can successfully act as immunogens. Peptide and non-protein antigens usually require coupling with a carrier protein to effectively function as an immunogen. This is due to their small molecular weight and the need for a carrier to provide a class II T receptor binding site. It may also be necessary to inject an adjuvant to ensure a high quality/quantity response. Adjuvants are non-specific stimuli of the immune response. The addition of an adjuvant not only reduces the dose of the antigen used, but also increases the durability of the antibody reaction.
Abcam hybridoma cell culture

[polyclonal antibody preparation]
A polyclonal antibody is prepared by inducing an immune response by antigen X. Repetitive use of the same antigen every few weeks to induce an immune response stimulates specific B cells to secrete large amounts of anti-X antibodies in the blood. Since many different B cells are stimulated by antigen X, various anti-X antibodies will be included in the blood, and their binding to X is slightly different. Crude immune sera with high levels of specific antibodies can be used directly, and specific antibodies can be isolated from serum components by affinity purification techniques.
[Monoclonic antibody preparation]
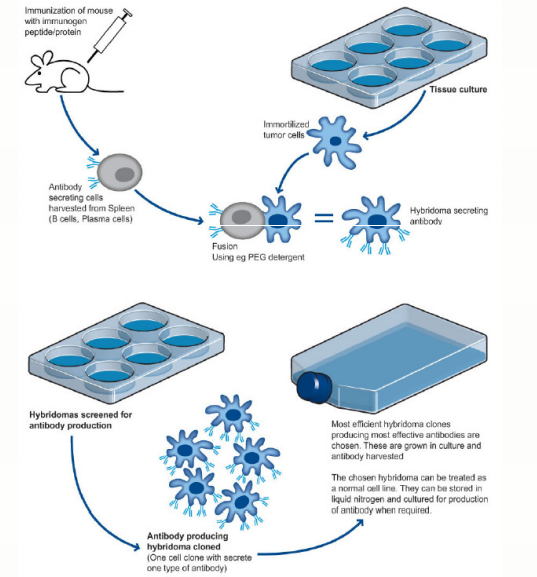
To prepare a monoclonal antibody, the same immunization protocol is used and all antibody-forming cells are extracted. These cells are fused with immortal tumor cells to form hybridoma cells, which are then screened for antibody preparation. The antibody-producing hybridoma cells are each given a unique clone name for easy identification. The antibody-producing hybridoma cells are cloned by isolation, followed by culture by tissue culture or by production of ascites in mice. Unlike polyclonal antibodies, monoclonal antibodies are homogeneous antibodies with well-defined specificity. Antibodies secreted by such cells can be obtained from the culture medium. The crude tissue culture supernatant can be used, or the supernatant can be further purified using affinity purification techniques.
Our company is a designated Abcam brand antibody agent, the price is fair and the quality is good! Also using technical guidance services, Shanghai Hengyuan Bio provides you with genuine Abcam antibody reagents.
Shower Hinge is a general type of door hinge largely applied for Glass Door, Shower Room. JIANGYI has specialized in door hinges since 2000, our hinges could pass 24 hours neutral salt spraying test and acid spraying test. Also, we specially use V groove spindle to make sure glass doors accurately stop at 0°and 90°.
Specification
1. Material: Brass/ Stainless Steel/ Zinc. Alloy
2. Finish: Mirror / Matt / Antique/ Red copper / Gold / Rose gold
3. Suitable for glass door width: 800-1000mm
4. Suitable for glass thickness: 8-10mm, 6mm/ 12mm
5. Load weight: 45kgs
6. Automatically close at Approximately 25°
7. Must be tempered glass
Shower Hinge
Shower Hinge,Glass Hinges,Shower Door Hinges,Shower Screen Hinges
Jiangyi Industrial Co., Ltd , https://www.cnjyhardware.com