Recently, scientists at Pennsylvania State University are developing a method for 3D printing of the "structural framework" of artificial tissue using commercial desktop 3D printing technology . The process involves enhancing cell injection of hydrogel material with support for 3D printed fiber optic networks.
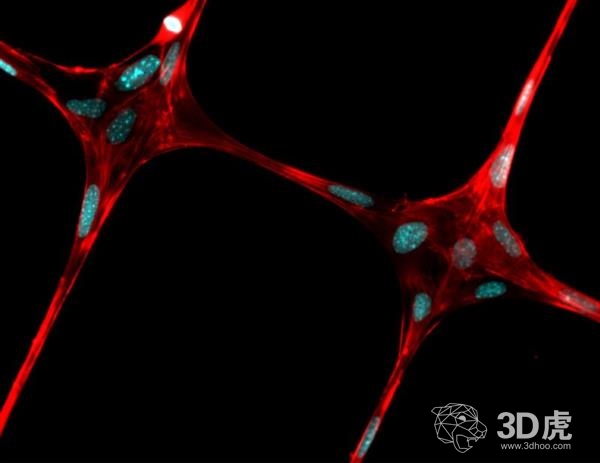
The researchers say that fiber printing can play a structural role in implantable hydrogels, in a sense, like steel reinforcements in cement. Justin L. Brown, an associate professor of biomedical engineering in Pennsylvania, added: "If we can make gels with some structure, we can grow living cells in a defined pattern, and eventually the fibers will dissolve and disappear."
However, the most notable aspect of the research project is that it is using affordable, off-the-shelf 3D printing technology to advance bio 3D printing.
As the researchers set out, their innovative technology combines desktop 3D printing technology with electrospinning technology, a process that uses electricity to produce nano-sized threaded fibers from a molten polymer or polymer solution. This combination allows for the creation of high resolution and repeatable 3D polymer fiber patterns for tissue engineering on non-conductive materials.
With these nano-threaded stents, researchers were able to demonstrate the growth of cells on them and successfully deposit these structures into the collagen-infused collagen hydrogel material.
The goal of this research was to create a convenient and low-cost way to produce complex human tissue with implant potential.
Biosciences doctoral student PouriaFattahi explained: "The general idea is that if we can combine collagen gel and bioprinting into electrospinning, we can build large and complex tissue interfaces, such as bones to cartilage. Others use micro-crowding Pressure bio-printers make these combinations."
However, it has been reported that the process of using a micro-extrusion bioprinter prints different tissue types separately and then combines them using an adhesive or a connector. Researchers at Penn State University believe that their 3D printed structural approach can better simulate how real tissues grow together in the body.
For example, the researchers say they can simply modify the pattern of the threaded structure to allow for a "seamless" transition between muscle tissue and tendons. Two different types of tissue - muscle and tendon tissue can be in a single print.
Of course, there is still work to be done before the organization of 3D printing can be implanted.
At this stage of the study, the team is measuring 3D printed less than one inch of the stent structure, which may be used to create ACL tissue found on the knee. Fattahi explained: "The anterior cruciate ligament or ACL is only 2 to 3 cm (0.8 to 1 inch) long and 1 cm (0.8 inch) wide."
It is reported that the research project has been funded by the National Institutes of Health. The findings have recently been published in the journal Advanced Health Care Materials.
Plastic Water Bottle is made of high-quality food grade plastic, safe and non-toxic. Compared with metal, it is more lightweight and portable. When the beverage is at room temperature, the hand feeling will be better than the metal water bottle.
And it is easy to process into a special shape to make the bottle more characteristic, and it is also easy to print. It can become your favorite color or pattern.
Plastic Water Bottle,Stainless Steel Bottom Plastic Bottle,Heat Transfer Printing Plastic Bottle,Plastic Flip Lid Bottle
Ningbo Auland International Co.,Ltd. , https://www.eversportsbottle.com